If you’re new to laser engraving, you’ve probably seen two terms pop up often: raster engraving and vector engraving.
Both are essential to creating high-quality laser projects, but they work very differently. Understanding their differences will help you:
- Choose the right mode for your project
- Improve engraving efficiency and quality
- Combine modes for creative and professional results
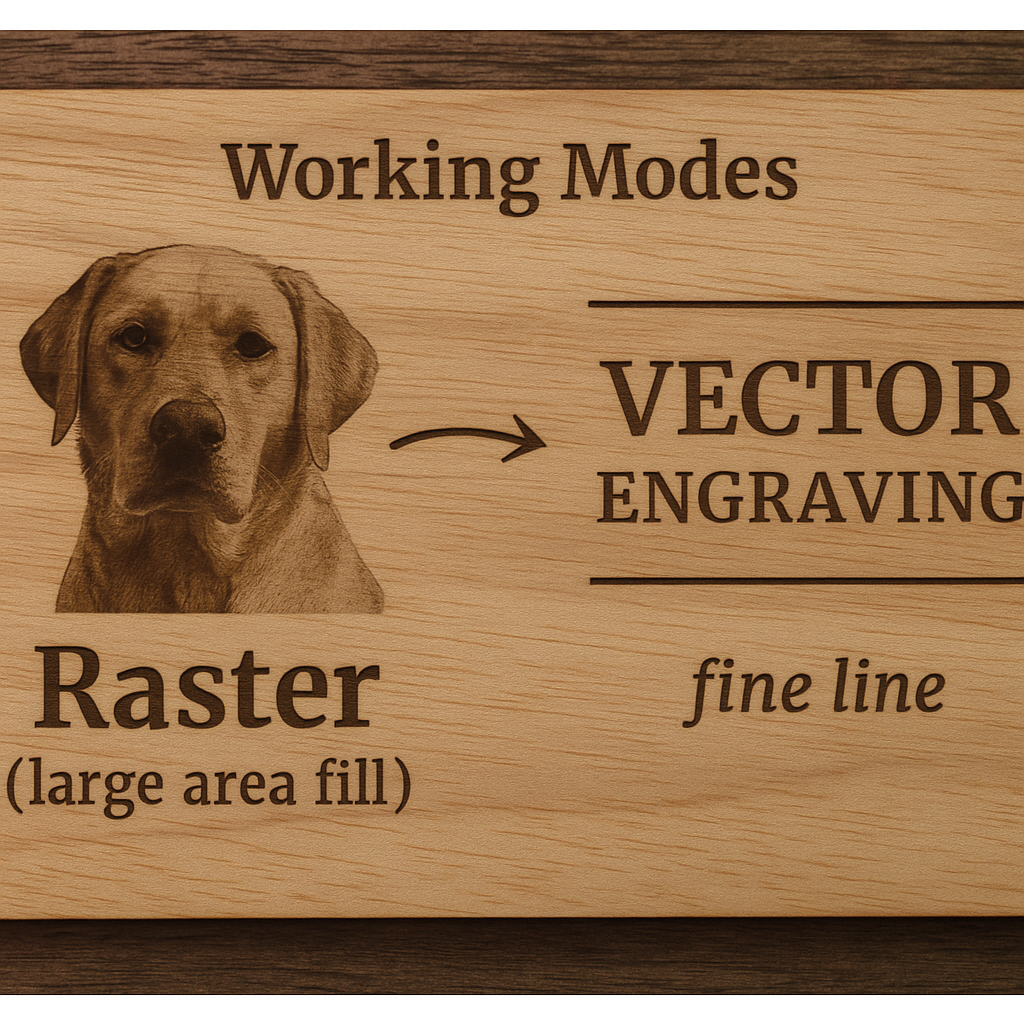
1️⃣ What Is Raster Engraving?
Raster engraving is like how a printer works—your laser moves back and forth across the surface line by line, firing where it needs to remove material.
Best for:
- Photos, logos, and bitmap graphics
- Large filled areas or designs with shading and gradients
Key Characteristics:
- High detail – Perfect for photos, portraits, or fine textures
- Slower speed – Laser must scan the entire area, even empty space
- Surface engraving only – Great for visual impact but not for cutting
💡 Example projects:
- Wooden photo frames with engraved images
- Acrylic plaques with gradient-filled logos
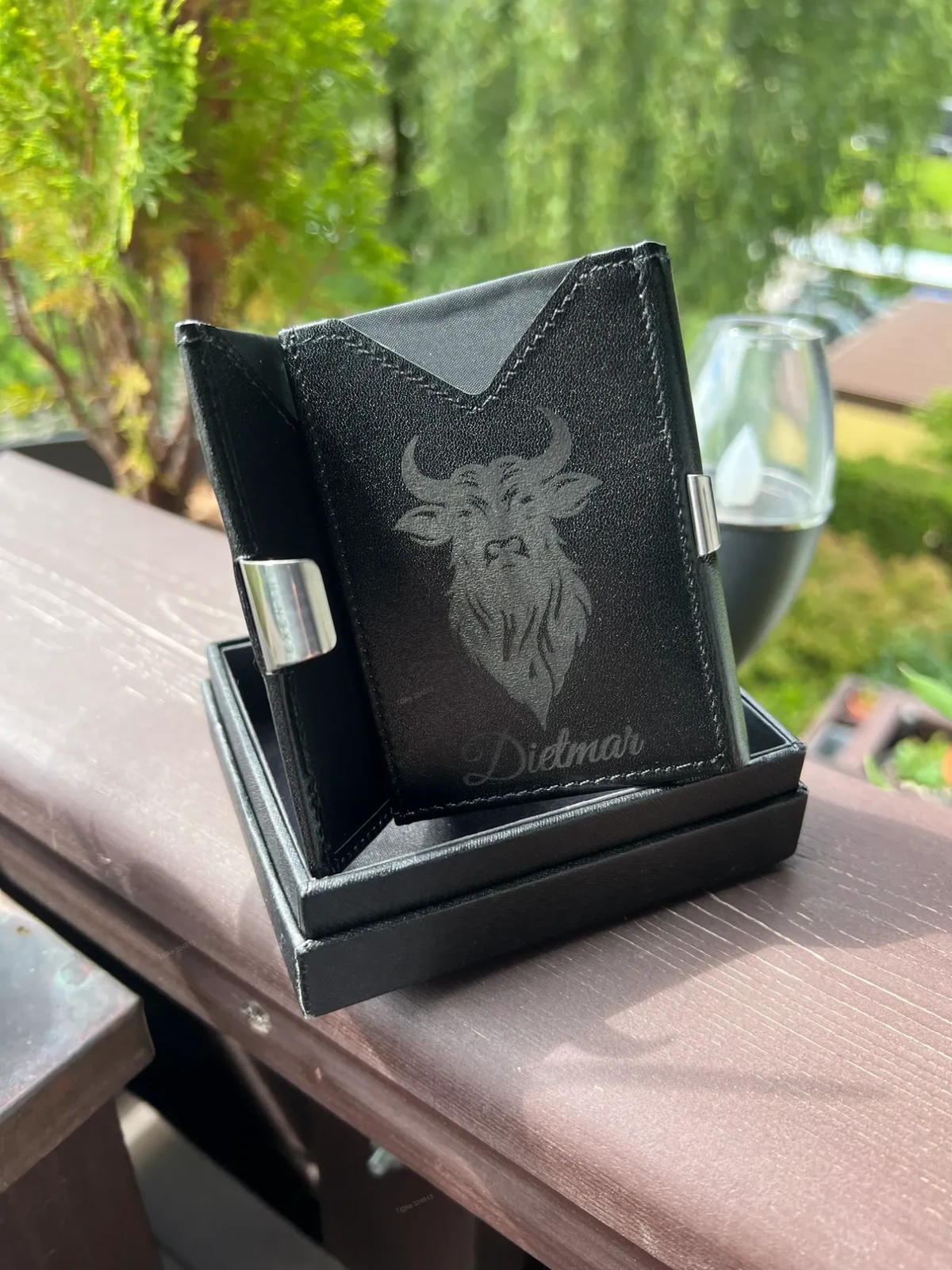
- Leather wallets with decorative patterns
2️⃣ What Is Vector Engraving?
Vector engraving (sometimes called line engraving) is when the laser follows the exact vector paths of your design, like a pen drawing a line.
Best for:
- Text, signatures, and simple line art
- Outlines, borders, or pre-cutting marks
Key Characteristics:
- Fast – The laser only travels along the defined lines
- Clean, sharp lines – Ideal for small lettering or minimalistic designs
- Can double as cutting if you increase power and reduce speed
💡 Example projects:
- Metal nameplates with etched outlines
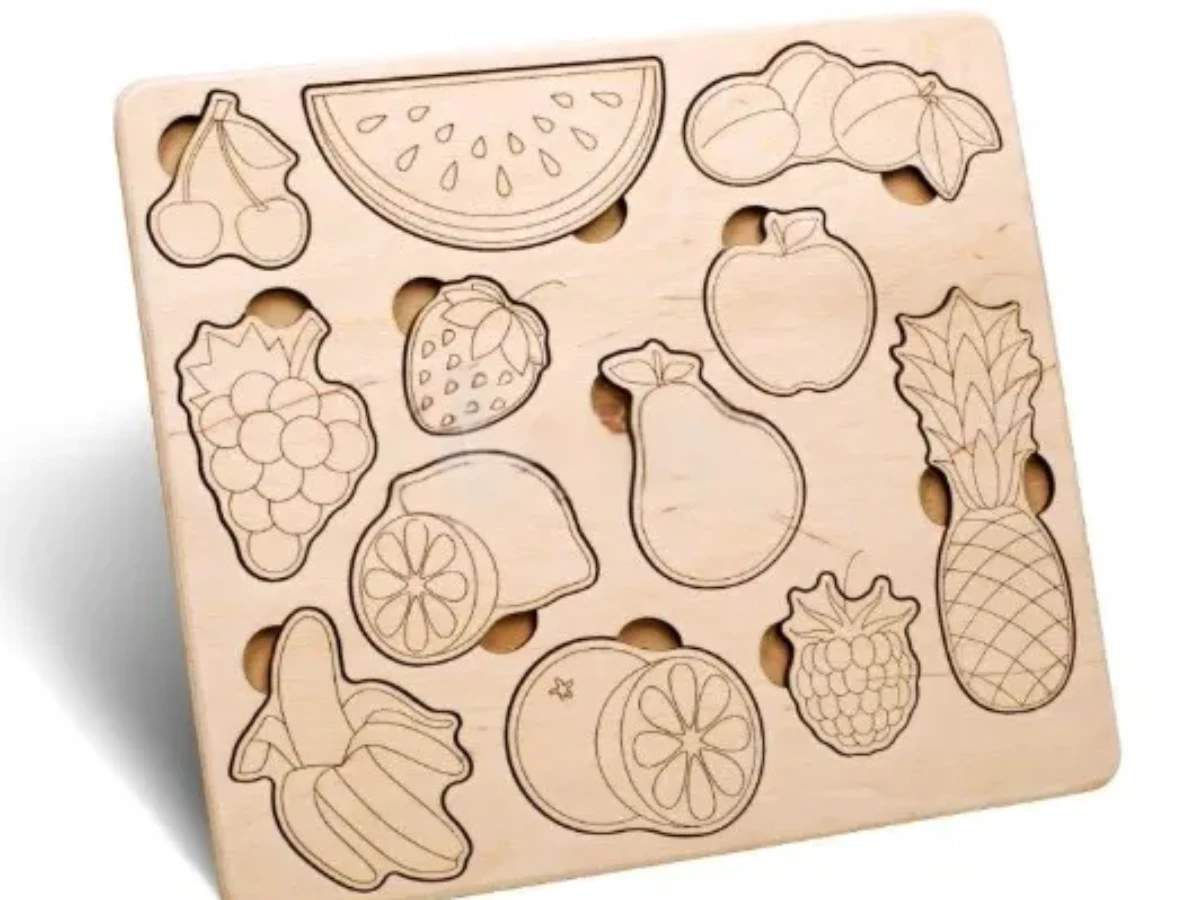
- Wooden puzzles or model outlines
- Jewelry or keychains with signature engravings
3️⃣ Raster vs Vector Engraving – Key Differences
Here’s a quick summary of how they compare:
Motion:
- Raster = back-and-forth scanning
- Vector = follows path lines directly
Speed:
- Raster = slower (covers whole area)
- Vector = faster (only follows lines)
Use Cases:
- Raster = photos, shading, large fills
- Vector = text, outlines, precise linework
Depth:
- Raster = shallow surface engraving
- Vector = lines can be engraved or cut
💡 Pro Tip: In LightBurn or similar software, you can combine both modes:
- Raster for filled logos or photos
- Vector for outlines or borders
This gives professional results in a single job.
4️⃣ When to Use Raster, Vector, or Both
Raster Only:
- Photo engravings on wood or acrylic
- Decorative leather patches
- Awards and plaques with filled text
Vector Only:
- Outlines for cutting or scoring
- Simple logos or single-line signatures
- Fast production marking
Combined Workflow:
- Logos with filled raster centers and vector outlines
- Layered wood or acrylic signs
- Engraved and cut ornaments or keychains
5️⃣ FAQs
Q: Can I cut with raster engraving?
A: No. Raster is for surface marking. Cutting requires vector paths with proper power and speed.
Q: Which mode is better for photos?
A: Raster engraving. It captures shading and details that vector cannot.
Q: Can I engrave text using raster mode?
A: Yes, but small text is faster and sharper with vector engraving.
Conclusion
Both raster and vector engraving are essential tools for laser creators:
- Raster delivers detailed images and shaded artwork
- Vector produces crisp lines, text, and cut-ready outlines
Once you learn how to combine both modes, you’ll create professional, efficient, and versatile laser projects.
✨ Want to see real raster and vector projects, with settings and files? Visit the Atomm Community to learn from other makers and download inspiration.